The Command Descriptions.
Page 1

Feet and Inch Plus.
Type: Math Command
Description: Feet and inch addition command used to add numbers in the feet and inch display format.
Takes the argument in level 1 and adds it to the argument in level 2. The result is returned
in level 1. The arguments must be in feet and inch format, unless the denominator is set to metric.
| Level 2/Argument 1 |
Level 1/Argument 2 |
 |
| Dimension |
Dimension |
 |

Feet and Inch Minus.
Type: Math Command
Description: Feet and inch subtraction command used to subtract numbers in the feet and inch display format.
Takes the argument in level 1 and subtracts it from the argument in level 2. The result is returned
in level 1. The arguments must be in feet and inch format, unless the denominator is set to metric.
| Level 2/Argument 1 |
Level 1/Argument 2 |
 |
| Dimension |
Dimension |
 |

Feet and Inch Multiply.
Type: Math Command
Description: Feet and inch multiplication command used to multiply numbers in the feet and inch display format.
Takes the argument in level 1 and multiplies it by the argument in level 2. The result is returned
in level 1. The arguments must be in feet and inch format, unless the denominator is set to metric.
| Level 2/Argument 1 |
Level 1/Argument 2 |
 |
| Dimension |
Dimension |
 |

Feet and Inch Divide.
Type: Math Command
Description: Feet and inch division command used to divide numbers in the feet and inch display format.
Takes the argument in level 1 and divides it by the argument in level 2. The result is returned
in level 1. The arguments must be in feet and inch format, unless the denominator is set to metric.
| Level 2/Argument 1 |
Level 1/Argument 2 |
 |
| Dimension |
Dimension |
 |

Convert to Decimal.
Type: Math Command
Description: Converts a number in feet and inch format to decimal feet. Takes the argument in level 1 and returns the result in level 1.
The argument must be in feet and inch format, unless the denominator is set to metric. When set to metric there is no conversion and the
argument is left unchanged.
| Level 1/Argument 1 |
 |
Level 1/Item 1 |
| Dimension |
 |
Decimal |

Convert to Feet and Inches.
Type: Math Command
Description: Converts a number in decimal feet to the feet and inch format. Takes the argument in level 1 and returns the result in level 1.
The argument must be in decimal feet, unless the denominator is set to metric. When set to metric there is no conversion and the
argument is left unchanged.
| Level 1/Argument 1 |
 |
Level 1/Item 1 |
| Decimal |
 |
Dimension |
Page 2


Base to Rise.
Type: Trigonometry Command
Description: Converts the base dimension of a right triangle to the rise dimension of the triangle. The command uses the
value in the angle variable for the acute angle of the right triangle. It takes the argument in level 1 and
returns the result in level 1. The arguments must be in feet and inch format, unless the denominator is set to metric.
| Level 1/Argument 1 |
 |
Level 1/Item 1 |
| Base |
 |
Rise |

Base to Slope.
Type: Trigonometry Command
Description: Converts the base dimension of a right triangle to the slope dimension of the triangle. The command uses the
value in the angle variable for the acute angle of the right triangle. It takes the argument in level 1 and
returns the result in level 1. The arguments must be in feet and inch format, unless the denominator is set to metric.
| Level 1/Argument 1 |
 |
Level 1/Item 1 |
| Base |
 |
Slope |

Rise to Base.
Type: Trigonometry Command
Description: Converts the rise dimension of a right triangle to the base dimension of the triangle. The command uses the
value in the angle variable for the acute angle of the right triangle. It takes the argument in level 1 and
returns the result in level 1. The arguments must be in feet and inch format, unless the denominator is set to metric.
| Level 1/Argument 1 |
 |
Level 1/Item 1 |
| Rise |
 |
Base |

Rise to Slope.
Type: Trigonometry Command
Description: Converts the rise dimension of a right triangle to the slope dimension of the triangle. The command uses the
value in the angle variable for the acute angle of the right triangle. It takes the argument in level 1 and
returns the result in level 1. The arguments must be in feet and inch format, unless the denominator is set to metric.
| Level 1/Argument 1 |
 |
Level 1/Item 1 |
| Rise |
 |
Slope |

Slope to Rise.
Type: Trigonometry Command
Description: Converts the slope dimension of a right triangle to the rise dimension of the triangle. The command uses the
value in the angle variable for the acute angle of the right triangle. It takes the argument in level 1 and
returns the result in level 1. The arguments must be in feet and inch format, unless the denominator is set to metric.
| Level 1/Argument 1 |
 |
Level 1/Item 1 |
| Slope |
 |
Rise |

Slope to Base.
Type: Trigonometry Command
Description: Converts the slope dimension of a right triangle to the base dimension of the triangle. The command uses the
value in the angle variable for the acute angle of the right triangle. It takes the argument in level 1 and
returns the result in level 1. The arguments must be in feet and inch format, unless the denominator is set to metric.
| Level 1/Argument 1 |
 |
Level 1/Item 1 |
| Slope |
 |
Base |
Page 3

Rise and Base to Angle.
Type: Trigonometry Command
Description: Calculates the angle, bevel, and slope of a right triangle from the rise and base dimensions.
This command takes the base argument in level 1 and the rise argument in level 2 and returns
the bevel in level 3, the slope in level 2 and the angle in level 1. The angle is also stored in the
angle variable that is used by the trigonometry commands on page 2. The bevel result is the rise of a right
triangle with a base of 12". The arguments must be in feet and inch format, unless the denominator is set to metric.

| Level 2/Argument 1 |
Level 1/Argument 2 |
 |
| Rise |
Base |
 |
| Level 3/Item 1 |
Level 2/Item 2 |
Level 1/Item 3 |
| Bevel |
Slope |
Angle |

Rise and Slope to Angle.
Type: Trigonometry Command
Description: Calculates the angle, bevel, and base of a right triangle from the rise and slope dimensions.
This command takes the slope argument in level 1 and the rise argument in level 2 and returns
the bevel in level 3, the base in level 2 and the angle in level 1. The angle is also stored in the
angle variable that is used by the trigonometry commands on page 2. The bevel result is the rise of a right
triangle with a base of 12". The arguments must be in feet and inch format, unless the denominator is set to metric.
| Level 2/Argument 1 |
Level 1/Argument 2 |
 |
| Rise |
Slope |
 |
| Level 3/Item 1 |
Level 2/Item 2 |
Level 1/Item 3 |
| Bevel |
Base |
Angle |

Base and Slope to Angle.
Type: Trigonometry Command
Description: Calculates the angle, bevel, and rise of a right triangle from the base and slope dimensions.
This command takes the slope argument in level 1 and the base argument in level 2 and returns
the bevel in level 3, the rise in level 2 and the angle in level 1. The angle is also stored in the
angle variable that is used by the trigonometry commands on page 2. The bevel result is the rise of a right
triangle with a base of 12". The arguments must be in feet and inch format, unless the denominator is set to metric.
| Level 2/Argument 1 |
Level 1/Argument 2 |
 |
| Rise |
Slope |
 |
| Level 3/Item 1 |
Level 2/Item 2 |
Level 1/Item 3 |
| Bevel |
Base |
Angle |

Calculate Bevel.
Type: Trigonometry Command
Description: Calculates the bevel on 12" using the angle that is currently stored in the angle variable.
It takes no arguments and returns the bevel result in level 1. The bevel result is the rise of a right
triangle with a base of 12", unless the denominator is set to metric. If set to metric, the bevel result
is the rise of a right triangle with a base of 1.
| Level 1/Argument 1 |
 |
Level 1/Item 1 |
| Nothing |
 |
Bevel |

Store Angle.
Type: Trigonometry Command
Description: Stores the number in level 1 of the stack in the angle variable. This provides quick access to the
angle variable used by the trig commands. It takes the angle argument in level 1 and returns the
angle result in level 1.
| Level 1/Argument 1 |
 |
Level 1/Item 1 |
| Angle |
 |
Angle |

Recall Angle.
Type: Trigonometry Command
Description: Recalls the number stored in the angle variable to level 1 of the stack. This provides quick access to the
angle variable used by the trig commands. It takes no arguments and returns the angle result in level 1.
| Level 1/Argument 1 |
 |
Level 1/Item 1 |
| Nothing |
 |
Angle |
Page 4

Store in Accumulator.
Type: Math Command
Description: Stores the feet and inch number in level 1 of the stack, into the Accumulator variable and displays the
current value of the accumulator in a message box. It takes a feet and inch argument in level 1 and returns
the feet and inch number stored in the accumulator.
The accumulator is a storage tool for accumulating the feet
and inch results of several calculations. With it you can, store a feet and inch number, add a positive or negative
feet and inch number, or recall it to level 1 of the stack. The arguments must be in feet and inch format,
unless the denominator is set to metric.
| Level 1/Argument 1 |
 |
Level 1/Item 1 |
| Dimension |
 |
Dimension |

Store Add Accumulator.
Type: Math Command
Description: Adds the feet and inch number in level 1 of the stack to the Accumulator variable and displays the
result value of the accumulator in a message box. It takes a feet and inch argument in level 1 and returns
the feet and inch result stored in the accumulator.
You can subtract a dimension by changing the sign of the number
before using this command. The arguments must be in feet and inch format, unless the denominator is set to metric.
| Level 1/Argument 1 |
 |
Level 1/Item 1 |
| Dimension |
 |
Dimension |

Recall the Accumulator.
Type: Math Command
Description: Recalls the feet and inch number stored in the accumulator variable to level 1 of the stack and displays the
value of the accumulator in a message box. It takes no arguments and returns the feet and inch number stored
in the accumulator.
| Level 1/Argument 1 |
 |
Level 1/Item 1 |
| Nothing |
 |
Dimension |

Table Clear.
Type: Storage Command
Description: Clears or creates the angle and dimension storage table. This command erases any existing data stored in your table. It will display
a choose box asking if you are sure you wish to proceed. It takes no arguments and returns no arguments.
The angle and
dimension storage table allows you to store dimensions and angles using a cell index number. The size of the table is limited only
by memory. This command creates an array with 100 cells and stores it using the name 'tbdat'. Each cell is referenced with an index
number starting with 1. The commands 'tbsto' & 'tbrcl' are used to store and recall dimensions and angles to and from the table.
The size of the variable 'tbdat' can be changed using intrinsic calculator commands.
| Level 1/Argument 1 |
 |
Level 1/Item 1 |
| Nothing |
 |
Nothing |

Table Store.
Type: Storage Command
Description: Stores an angle or dimension in the dimension and angle storage table using a cell index number. It takes
the angle or dimension argument in level 2 and the index argument in level 1 and returns the angle or dimension that was stored
in level 1 of the stack.
Be sure to write down the index number next to the dimension or angle on your design document so
that you can quickly recall the number at a later time. Your stored number will retain the full precision of your original calculation.
You can use the index numbers 1 thru 100 without modifying the size of the table.
| Level 2/Argument 1 |
Level 1/Argument 2 |
 |
| Angle or Dim |
Index |
 |
| Level 1/Item 1 |
| Angle or Dim |

Table Recall.
Type: Storage Command
Description: Recalls an angle or dimension from the dimension and angle storage table using a cell index number. It takes
the index argument in level 1 and then asks if you would like the number recalled, to be stored in the angle
variable. If you answer yes the angle is stored in the angle variable and is returned to level 2 and the bevel
on 12" is returned to level 1. If you answer no then the angle or dimension is just returned to level 1.
The dimension and angle storage table gives you 100 memory locations to store your data. Each location is identified
by an index number so you can quickly recall the data you need for your calculations. You can view and edit the 'tbdat'
variable with Matrix Writer. A copy of the variable 'tbdat' can be saved to port memory or your PC for backup or future use.
| Level 2/Argument 1 |
Level 1/Argument 2 |
 |
| Angle or Dim |
Index |
 |
| Level 1/Item 1 |
| Angle or Dim |
Page 5

Arc Angle.
Type: Circular Geometry Command
Description: Calculates the included angle given the arc length and radius in feet and inches. It prompts you for the arc length
and radius, displays the angle in a message box, and returns the angle to level 1. Variables can be used as input.
The arguments must be in feet and inch format, unless the denominator is set to metric.
| Level 1/Argument 1 |
 |
Level 1/Item 1 |
| Nothing |
 |
Angle |

Arc Length.
Type: Circular Geometry Command
Description: Calculates the arc length given the radius in feet and inches and the included angle. It prompts you for the radius
and angle, displays the arc length in a message box, and returns the arc length to level 1. Variables can be used as
input. The radius argument must be in feet and inch format, unless the denominator is set to metric.
| Level 1/Argument 1 |
 |
Level 1/Item 1 |
| Nothing |
 |
Arc Length |

Chord and Rise to Radius.
Type: Circular Geometry Command
Description: Calculates the radius dimension given the chord and the rise in feet and inches. It prompts you for the chord
and the rise, displays the radius in a message box, and returns the radius to level 1. Variables can be used as
input. The arguments must be in feet and inch format, unless the denominator is set to metric.
| Level 1/Argument 1 |
 |
Level 1/Item 1 |
| Nothing |
 |
Radius |

Radius and Rise to Chord.
Type: Circular Geometry Command
Description: Calculates the chord dimension given the radius and the rise in feet and inches. It prompts you for the radius
and the rise, displays the chord in a message box, and returns the chord to level 1. Variables can be used as
input. The arguments must be in feet and inch format, unless the denominator is set to metric.
| Level 1/Argument 1 |
 |
Level 1/Item 1 |
| Nothing |
 |
Chord |

Radius and Chord to Rise.
Type: Circular Geometry Command
Description: Calculates the rise dimension given the radius and the chord in feet and inches. It prompts you for the radius
and the chord, displays the rise in a message box, and returns the rise to level 1. Variables can be used as
input. The arguments must be in feet and inch format, unless the denominator is set to metric.
| Level 1/Argument 1 |
 |
Level 1/Item 1 |
| Nothing |
 |
Rise |

Area of circle.
Type: Circular Geometry Command
Description: Calculates the area of a circle given the radius in feet and inches. It prompts you for the radius
, displays the area in a message box, and returns the area to level 1. Variables can be used as
input. The argument must be in feet and inch format, unless the denominator is set to metric.
| Level 1/Argument 1 |
 |
Level 1/Item 1 |
| Nothing |
 |
Area |
Page 6

Volume Weight.
Type: Weight Command
Description: Calculates the weight of a quantity of cubic areas of material using feet and inch or metric input. It prompts you
for the quantity, the thickness, the width, the length, and the weight per cubic unit. When running in feet and inches
mode the weight in pounds, of one cubic foot of steel (490 lbs.) is provided as a default input for the per cubic unit input.
When running in metric mode the weight in kilograms of one cubic millimeter of steel (0.00000784905 kg.) is provided as a default input for
the per cubic unit input. You can use these or enter your own values.
In feet and inch mode the result is labeled "lbs",
in metric mode the result is labeled "kg". You can disregard the label if your units are not kilograms or pounds. The
result is displayed in a message box and is returned to level 1 of the stack.The arguments must be in feet and inch format,
unless the denominator is set to metric.
| Level 1/Argument 1 |
 |
Level 1/Item 1 |
| Nothing |
 |
Weight |

Linear Weight.
Type: Weight Command
Description: Calculates the weight of a quantity of linear areas of material using feet and inch or metric input.
To use this command you need to know the weight per linear unit. It prompts you for the quantity, the length,
and the weight per linear unit. The result is displayed in a message box and is returned to level 1 of the stack.
The arguments must be in feet and inch format, unless the denominator is set to metric.
| Level 1/Argument 1 |
 |
Level 1/Item 1 |
| Nothing |
 |
Weight |

Square Weight.
Type: Weight Command
Description: Calculates the weight of a quantity of square areas of material using feet and inch or metric input.
To use this command you need to know the weight per square unit. It prompts you for the quantity, the width, the length,
and the weight per square unit. The result is displayed in a message box and is returned to level 1 of the stack.
The arguments must be in feet and inch format, unless the denominator is set to metric.
| Level 1/Argument 1 |
 |
Level 1/Item 1 |
| Nothing |
 |
Weight |

Feet to Inches.
Type: Conversion Command
Description: Converts a dimension from feet and inch format to inches and sixteenths, in the form of xxx.yy where xxx
equals the inches and yy equals the sixteenths. It takes the feet & inch argument in level 1 and returns
the inches in level 1. The argument must be in feet and inch format. You must be in a feet and inch mode to use this
command, in metric mode the result will not make sense.
| Level 1/Argument 1 |
 |
Level 1/Item 1 |
| Dimension |
 |
Inches |

Feet to Millimeters.
Type: Conversion Command
Description: Converts a dimension in feet and inch format to millimeters, It takes the feet and inch argument in level 1 and returns
the millimeters in level 1. The argument must be in feet and inch format. You must be in a feet and inch mode to use this
command, in metric mode the result will not make sense.
| Level 1/Argument 1 |
 |
Level 1/Item 1 |
| Dimension |
 |
Millimeters |

Millimeters to Feet.
Type: Conversion Command
Description: Converts a dimension in millimeters to feet and inch format. It takes the millimeters argument in level 1 and returns
the feet and inch argument in level 1. The argument must be in millimeters. You must be in a feet and inch mode to use this
command, in metric mode the result is returned as decimal feet.
| Level 1/Argument 1 |
 |
Level 1/Item 1 |
| Millimeters |
 |
Dimension |
Page 7

Side Side Side.
Type: Trigonometry Command
Description: Calculates the 3 angles of an oblique triangle given the three sides in feet and inch format. In addition this command
calculates the area and the weight of the triangle given the thickness in feet and inch format and the weight per cubic unit.
It prompts you for side c, side b, and side a, then returns side c, angle B, side b, angle A, side a, angle C, and the area in square
units. It then prompts you for the thickness and Weight per cubic unit. When running in feet and inches mode the weight in pounds, of
one cubic foot of steel (490 lbs.) is provided as a default input for the per cubic unit input. When running in metric mode the weight
in kilograms of one cubic millimeter of steel (0.00000784905 kg.) is provided as a default input for the per cubic unit input. You can use
these or enter your own values.
In feet and inch mode the result is labeled "lbs", in metric mode the result is labeled "kg". You
can disregard the label if your units are not kilograms or pounds. The results are displayed in message boxes and are returned to the stack
in the order they were displayed. The arguments must be in feet and inch format, unless the denominator is set to metric.
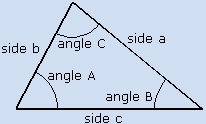
| Level 1 |
 |
Level 8 |
Level 7 |
Level 6 |
Level 5 |
| Nothing |
 |
side c |
angle A |
side b |
angle C |
| Level 4 |
Level 3 |
Level 2 |
Level 1 |
| side a |
angle B |
area |
weight |

Angle Side Angle.
Type: Trigonometry Command
Description: Calculates the remaining 2 sides and 1 angle of an oblique triangle given 1 angle, 1 side in feet and inch format, and 1 angle. In addition this command
calculates the area and the weight of the triangle given the thickness in feet and inch format and the weight per cubic unit.
It prompts you for angle B, side c, and angle A then returns side c, angle B, side b, angle A, side a, angle C, and the area in square
units. It then prompts you for the thickness and Weight per cubic unit. When running in feet and inches mode the weight in pounds, of
one cubic foot of steel (490 lbs.) is provided as a default input for the per cubic unit input. When running in metric mode the weight
in kilograms of one cubic millimeter of steel (0.00000784905 kg.) is provided as a default input for the per cubic unit input. You can use
these or enter your own values.
In feet and inch mode the result is labeled "lbs", in metric mode the result is labeled "kg". You
can disregard the label if your units are not kilograms or pounds. The results are displayed in message boxes and are returned to the stack
in the order they were displayed. The side argument must be in feet and inch format, unless the denominator is set to metric.

| Level 1 |
 |
Level 8 |
Level 7 |
Level 6 |
Level 5 |
| Nothing |
 |
side c |
angle A |
side b |
angle C |
| Level 4 |
Level 3 |
Level 2 |
Level 1 |
| side a |
angle B |
area |
weight |

Side Angle Angle.
Type: Trigonometry Command
Description: Calculates the remaining 2 sides and 1 angle of an oblique triangle given one side in feet and inch format and 2 angles. In addition this command
calculates the area and the weight of the triangle given the thickness in feet and inch format and the weight per cubic unit.
It prompts you for side c, angle A, and angle C then returns side c, angle B, side b, angle A, side a, angle C, and the area in square
units. It then prompts you for the thickness and Weight per cubic unit. When running in feet and inches mode the weight in pounds, of
one cubic foot of steel (490 lbs.) is provided as a default input for the per cubic unit input. When running in metric mode the weight
in kilograms of one cubic millimeter of steel (0.00000784905 kg.) is provided as a default input for the per cubic unit input. You can use
these or enter your own values.
In feet and inch mode the result is labeled "lbs", in metric mode the result is labeled "kg". You
can disregard the label if your units are not kilograms or pounds. The results are displayed in message boxes and are returned to the stack
in the order they were displayed. The side argument must be in feet and inch format, unless the denominator is set to metric.

| Level 1 |
 |
Level 8 |
Level 7 |
Level 6 |
Level 5 |
| Nothing |
 |
side c |
angle A |
side b |
angle C |
| Level 4 |
Level 3 |
Level 2 |
Level 1 |
| side a |
angle B |
area |
weight |

Side Angle Side.
Type: Trigonometry Command
Description: Calculates the remaining 1 sides and 2 angles of an oblique triangle given 1 side, 1 angle, and 1 side in feet and inch format. In addition this command
calculates the area and the weight of the triangle given the thickness in feet and inch format and the weight per cubic unit.
It prompts you for side c, angle A, and side b then returns side c, angle B, side b, angle A, side a, angle C, and the area in square
units. It then prompts you for the thickness and Weight per cubic unit. When running in feet and inches mode the weight in pounds, of
one cubic foot of steel (490 lbs.) is provided as a default input for the per cubic unit input. When running in metric mode the weight
in kilograms of one cubic millimeter of steel (0.00000784905 kg.) is provided as a default input for the per cubic unit input. You can use
these or enter your own values.
In feet and inch mode the result is labeled "lbs", in metric mode the result is labeled "kg". You
can disregard the label if your units are not kilograms or pounds. The results are displayed in message boxes and are returned to the stack
in the order they were displayed. The side argument must be in feet and inch format, unless the denominator is set to metric.

| Level 1 |
 |
Level 8 |
Level 7 |
Level 6 |
Level 5 |
| Nothing |
 |
side c |
angle A |
side b |
angle C |
| Level 4 |
Level 3 |
Level 2 |
Level 1 |
| side a |
angle B |
area |
weight |

Side Side Angle.
Type: Trigonometry Command
Description: Calculates the remaining 1 sides and 2 angles of an oblique triangle given 2 sides in feet and inch format and 1 angle.
In addition this command calculates the area and the weight of the triangle given the thickness in feet and inch format and
the weight per cubic unit. It prompts you for side c, side b, and angle Angle B then returns side c, angle B, side b, angle A, side a, angle C, and the area in square
units. It then prompts you for the thickness and Weight per cubic unit. When running in feet and inches mode the weight in pounds, of
one cubic foot of steel (490 lbs.) is provided as a default input for the per cubic unit input. When running in metric mode the weight
in kilograms of one cubic millimeter of steel (0.00000784905 kg.) is provided as a default input for the per cubic unit input. You can use
these or enter your own values.
In feet and inch mode the result is labeled "lbs", in metric mode the result is labeled "kg". You
can disregard the label if your units are not kilograms or pounds. The results are displayed in message boxes and are returned to the stack
in the order they were displayed. The side argument must be in feet and inch format, unless the denominator is set to metric.

| Level 1 |
 |
Level 8 |
Level 7 |
Level 6 |
Level 5 |
| Nothing |
 |
side c |
angle A |
side b |
angle C |
| Level 4 |
Level 3 |
Level 2 |
Level 1 |
| side a |
angle B |
area |
weight |

About.
Type: General Command
Description: Displays website URL, application name, and copyright notice. It takes no arguments and returns no arguments.
Press cancel to continue.
| Level 1/Argument 1 |
 |
Level 1/Item 1 |
| Nothing |
 |
Nothing |
Page 8

Set Denominator.
Type: Configuration Command
Description: Used to set the various modes of operation. The precision of the fractional part of your dimensions can
be set to halves, 4ths, 8ths, 16ths, 32nds, and 64ths of an inch. Choosing the metric setting disables
the feet and inch conversion and allows you to work in decimal units. This command displays a choose box
with the following options: Metric, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64. The default setting is 16 for working in sixteenths
of an inch. It takes no arguments and returns no arguments.
| Level 1/Argument 1 |
 |
Level 1/Item 1 |
| Nothing |
 |
Nothing |

Change Denominator.
Type: Conversion Command
Description: Changes the denominator of the fractional portion of a dimension. The precision of the fractional part
of your dimensions can be set to halves, 4ths, 8ths, 16ths, 32nds, and 64ths of an inch. It takes the argument
in level 1 and returns the result in level 1. The argument must be in feet and inch format and you
must be in a feet and inch mode.
| Level 1/Argument 1 |
 |
Level 1/Item 1 |
| Dimension |
 |
Dimension |

Show Denominator.
Type: Conversion Command
Description: Shows a dimension with the fractional portion changed to the denominator you select. The precision of the fractional part
of your dimensions can be set to halves, 4ths, 8ths, 16ths, 32nds, and 64ths of an inch. It takes the argument
in level 1 and returns it back to level 1 unchanged. The argument must be in feet and inch format and you
must be in a feet and inch mode. This command lets you view how your dimension appears in another mode without
changing it.
| Level 1/Argument 1 |
 |
Level 1/Item 1 |
| Dimension |
 |
Dimension |

Setup Variables.
Type: Setup Command
Description: Creates the global variables that are used by this application. You will need to run this command before
you can use the SFT Feet and Inch engineering tools. The names of the variables this command creates are:
sft49, CST, tbdat, dnom, acc1, and angle. It will not change or erase these variable if they exist, except for
the CST variable, in the case of the CST variable, it will add a menu command to activate the sftfi library menu. It checks
to make sure all the variables are present and creates them only if they do not exist in the current directory or a parent directory.
It takes no arguments and returns no arguments.
| Level 1/Argument 1 |
 |
Level 1/Item 1 |
| Nothing |
 |
Nothing |
Variable Descriptions.

sft49
Type: Program
Description: Program that activates the sftfi library menu. It provides access to the sftfi library from the variable menu
and is also used by the custom menu in the CST variable.

CST
Type: List
Description: Variable used to create a custom menu. The command

is used to activate the SFT Feet and Inch engineering tools menu.

tbdat
Type: Array
Description: Array variable with 100 cells. It is used to store the angle and dimension table.

dnom
Type: Real
Description: Real variable used to store the current denominator setting. You can use it to check the current setting

acc1
Type: Real
Description: Real variable used to store the current value of the accumulator. The value is stored as decimal feet.

angle
Type: Real
Description: Real variable used to hold the angle used by the right triangle trigonometry commands.
To Top of Page
![]() key and then press the
key and then press the ![]() key. This puts your calculator
in server mode. Start the PC Connectivity Kit and set the calculator mode to binary. Locate the file
"sft49.lib" on your PC and drag the file to
the home directory on your calculator. If you wish, you can disconnect your calculator from your
PC before you continue.
key. This puts your calculator
in server mode. Start the PC Connectivity Kit and set the calculator mode to binary. Locate the file
"sft49.lib" on your PC and drag the file to
the home directory on your calculator. If you wish, you can disconnect your calculator from your
PC before you continue.![]() key and
then press the menu key named
key and
then press the menu key named ![]() . Level 1 of the stack
should now contain the object named "Library 1780: sft49 F&I Engr Tools". Type the number of the port
you wish to store the library in (0, 1, or 2) then press the
. Level 1 of the stack
should now contain the object named "Library 1780: sft49 F&I Engr Tools". Type the number of the port
you wish to store the library in (0, 1, or 2) then press the ![]() key. Purge the variable
named "sft49.lib" from the home directory. Perform a system halt by
holding down
key. Purge the variable
named "sft49.lib" from the home directory. Perform a system halt by
holding down ![]() and pressing
and pressing ![]() .
.![]() list. You can activate the tools menu using the
list. You can activate the tools menu using the ![]()
![]()
![]() command. Use one of these methods to bring up the
SFT tools menu and then press
command. Use one of these methods to bring up the
SFT tools menu and then press ![]()
![]()
![]() . This command creates the required global variables in the current
directory and adds a command to your custom menu so you can activate the tools menu using the
. This command creates the required global variables in the current
directory and adds a command to your custom menu so you can activate the tools menu using the ![]() command in the custom menu
or the Variables menu. The South Fork Technologies Feet & Inch Engineering
Tools are now ready to use.
command in the custom menu
or the Variables menu. The South Fork Technologies Feet & Inch Engineering
Tools are now ready to use.